Diesel Fuel Injector Nozzles
Abstract: The fuel injector nozzle is critical to the performance and emissions of diesel engines. Some of the important injector nozzle parameters—including details of the injector seat, the injector sac and nozzle hole size and geometry—affect the combustion characteristics of the diesel engine, as well as the stability of the emissions and performance over the lifetime of the engine and the mechanical durability of the injector.
Design of the diesel fuel injector nozzle is critical to the performance and emissions of modern diesel engines. Some of the important injector nozzle design parameters include details of the injector seat, the injector sac and nozzle hole size and shape. These features not only affect the combustion characteristics of the diesel engine, they can also affect the stability of the emissions and performance over the lifetime of the engine and the mechanical durability of the injector.
All nozzles must produce a fuel spray that meets the requirements of the performance and emissions goals of the market for which the engine is produced regardless of details of the fuel system design (i.e., regardless if the fuel system is of the common rail, unit injector, unit pump or pump-line-nozzle type). Additionally, specific requirements for injection nozzles can also depend on the fuel system type [Potz 2000]:
Common rail—nozzle operates under more demanding tribological conditions and must be better designed to prevent leakage.
Unit injector/unit pump—pressure pulsing conditions create more demanding fatigue strength requirements.
Pump-line-nozzle—hydraulic dead volume must be minimized.
Figure 1. Basic Diesel Injector Nozzle with Single Cone Seat
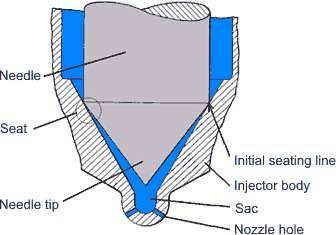
Figure 1 shows a basic overview of the major components of a diesel fuel injector nozzle [Parrish 1976]. Several of these components are discussed in detail in the following sections. Readers should also review the introduction to injector nozzles that was given in the paper on injection system components. |


![]()























