Injection can be initiated any time after the plunger starts its downward travel. But until the ECM signals the solenoid valve to close the spill/fill port, fuel merely cycles through the EUIs as a coolant and as a purge to remove any entrapped air.
Upon signal, the solenoid valve closes the port, trapping fuel in the injector barrel. Further downward movement of the plunger raises fuel pressure sufficiently to overcome spring tension acting on the check valve. The check valve opens and injection begins.
Injection continues until the ECM signals the solenoid to open the spill/fill port. Responding to the sudden loss of pressure at the injector tip, the check valve snaps shut. Injection ceases. The plunger continues its downward stroke, displacing fuel through the open spill/fill port and into the fuel-return gallery.
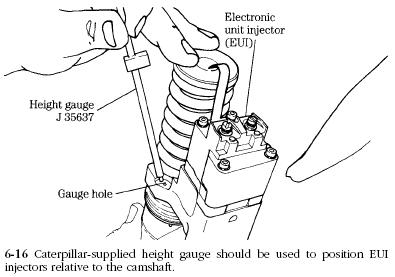
Although the software has primary responsibility for injector timing, plunger movement is affected by rocker-arm lash. The onset of pressure rise depends upon the clearance between the rocker arm and the plunger. A Caterpillar PN J 35637 height gauge is used to establish this critical variable (Fig. 6-16).
EUI position Caterpillar EMS Electronic Unit Injector
|


![]()























